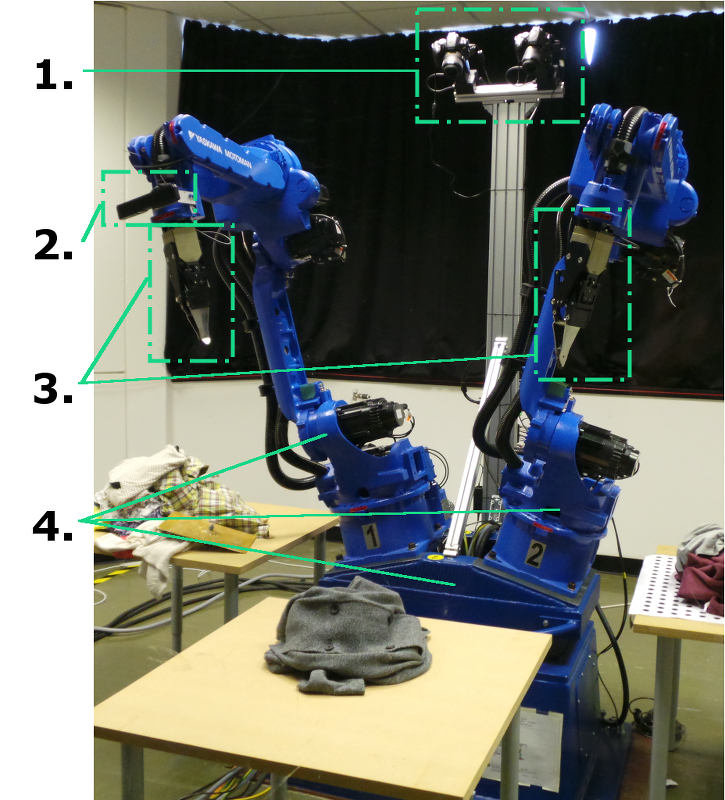
Overview of the CloPeMa robot
One of the novelty challenges in CloPeMa was to design a clothes folding prototype robot from (mainly) off-the-shelf components. There are now three CloPeMa prototype robots hosted in three different European countries: Czech Republic (CVUT), Greece (CERTH) and Glasgow (UG). The robot prototype has been setup with a variety of components, such as Xtions, Cameras, force sensor or photometric close-range sensors. All the different parts of the robot system are integrated in and operate with Robot Operating System (ROS).
(for description scroll down)
1. Robot binocular-vision head
The robot head comprises two Nikon DSLR cameras (D5100) that are capable of capturing images at 16 mega pixels. These are mounted on two pan and tilt units (PTU-D46) with their corresponding controllers. The cameras are separated by a pre-defined baseline for optimal stereo capturing. Its position enables imaging the robot work-space from above. The head provides the robot system with high resolution 3D points clouds.
2. Xtion
The robot has been fitted with two to three Xtion Pro Live from ASUS for light weight range sensing, one on each arm and depending the sights one on the back spine. They are in use for for recognition and manipulation planning. CERTH are using Xtion to recognize the type of clothing held up by the robot, find grasping key points and CVUT plans the movement of clothes folding.
3. Grippers
3.1. Prototype grippers and tactile sensor
The University of Genoa (UNIGE) has developed for CloPeMa prototype grippers for grasping clothes based of Schunk grippers. The prototype has a tactile sensor at the “finger tips” to sense the garment material using little rubbing motions between the “gripper fingers”. Fitted with the multi-modal tactile sensor it can also detect proximity, sound and pressure in order sense buttons and other smaller details of clothing. Furthermore the gripper has patented variable stiffness actuators for adapting to different grasping and steering tasks.
3.2. Photometric Stereo gripper-mounted sensor
CERTH has designed a small scale stereo-pair camera sensor that fits into the “palm” of the gripper (height: 39.5 mm, diameter: 39 mm). Stable mounting is achieved using only four screws (see image). It uses auto-focus, has adjustable LED intensity and is fully parameterisable for exposure time, white balance, focus and other features. The sensors captures at 1280×800 px resolution and has software support to do 3D reconstruction of close-range garment surface. The full capture process, i.e. focusing, capturing and reconstruction, requires less than 7 seconds. Mainly used for black and white images, it can also capture color images. The LED-ring is optional and can be removed if not required.

(left) Gripper with integrated photometric stereo; (right) Photometric stereo sensor capturing close-range surface
3.3. Wrist Force/Torque sensor (only in CVUT)
Exclusively at CVUT a ATI six-axis force/torque sensor (ATI Mini45 FT) is integrated in the wrist of one gripper. It is used to sense for contact of the gripper with table and for feedback for the robot system when stretching out a held-up piece of clothing. A new feature in the system is, based on the force/torque sensor, a user can guide the robot arm into a desired position by pushing and pulling lightly the robot arm wrist.
4. Robot body
The robot body is based on robotics components used in the welding industry supplied by YASKAWA Motoman. The robot has two MA1400 arms, attached to a by Motoman tailor made turn table on a base and is powered and piloted by a control unit DX100.